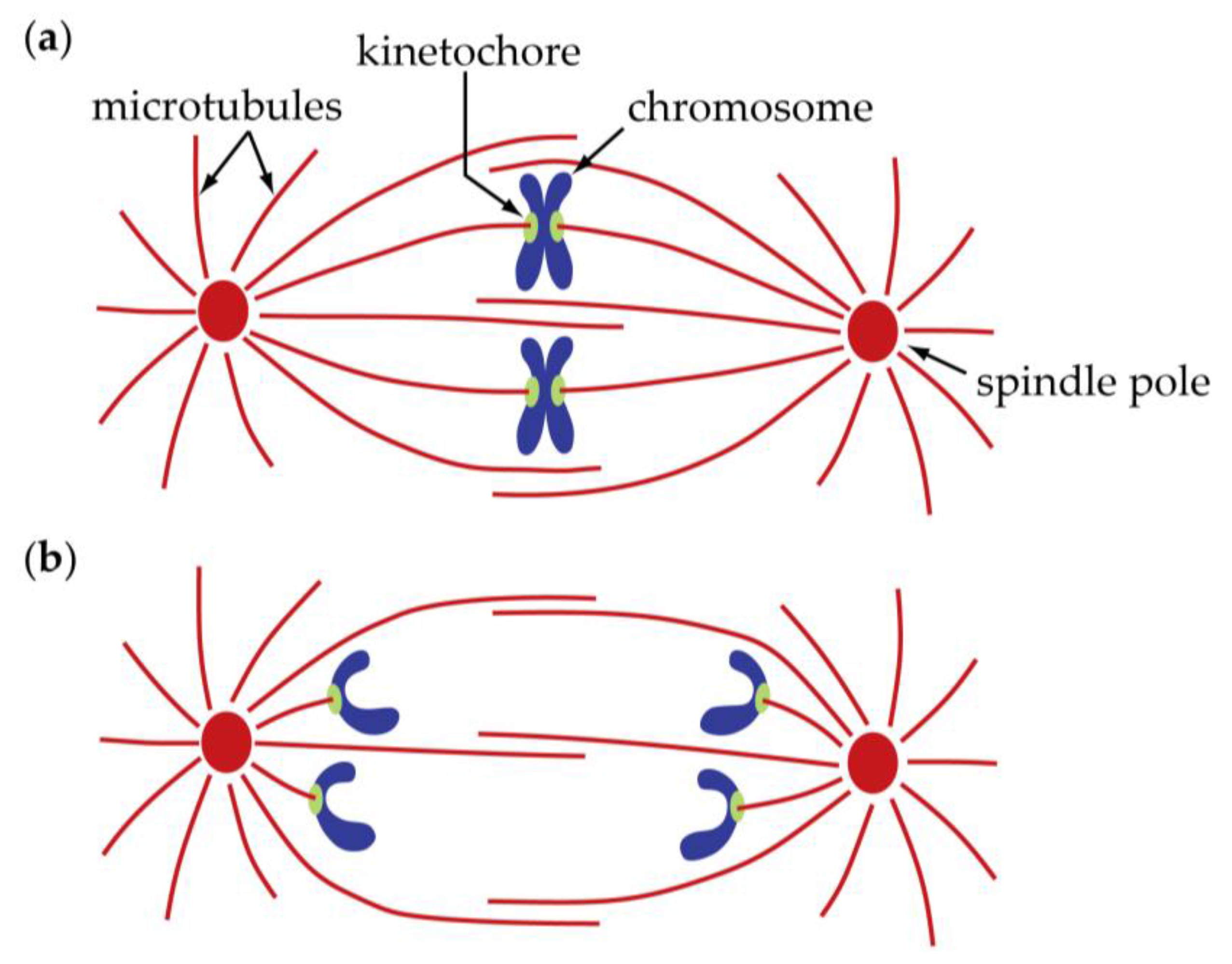
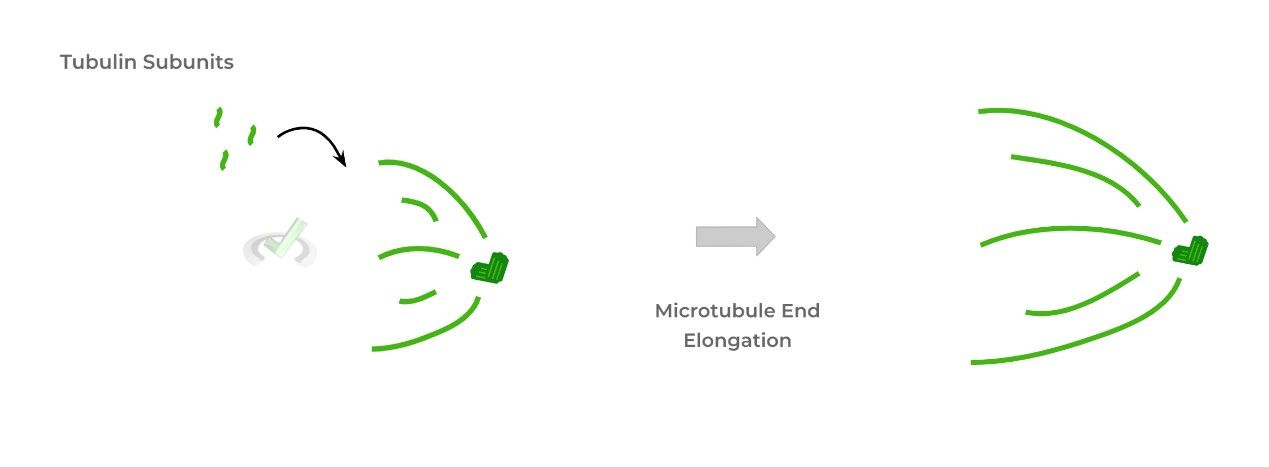
Mitosis Structures and Processes on the MCAT MedLife Mastery Biology Diagrams In prophase 1, spindle fibers attach to homologous chromosomes, while in prophase 2, they reorient to attach to sister chromatids. This reorientation is crucial for the segregation of chromatids during anaphase 2. Research highlights the importance of these proteins, illustrating how their malfunction can lead to aneuploidy, which affects Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Cells with _____ have a higher chance of increasing a person's risk of developing cancer. -old DNA -damaged DNA -physical damage, Once meiosis II has completed, the resulting cells are _____. -genetically identical -genetically unique -always physically unique, During anaphase I, _____ are separated. -homologous chromosomes Spindle fiber is a network of filaments that are formed during the cell division process. They help in the movement of chromosomes during both mitosis and meiosis. Q2 . What are spindle fibers made of? Spindle fiber is most abundantly composed of the microtubule, which is a polymer of 𝜶 and 𝞫-tubulin dimer. Also, the spindle fiber is made
Spindle fibers pull the chromosomes toward the equator. This creates tension and aligns them in a straight line. This precise alignment ensures each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. Any malfunction can lead to genetic disorders. By learning about it, we appreciate the complexity of life. Knowledge of spindle apparatus

Mitotic spindle (DIS)orientation and DISease: Cause or consequence? Biology Diagrams
Spindle fibers play a significant role in mitosis. They remain highly active during this phase and equally divide the chromosomes in a parental cell into two daughter cells. Let us discuss the role of spindle fibers in each step of mitosis. Prophase. Spindle fibers start to form the centrioles at the opposite poles of the cell. The spindle is formed during prophase of mitosis and meiosis, and its role is crucial for the correct separation of chromosomes. Components of the Spindle. The spindle is composed of three main components: Microtubules: These are the primary building blocks of the spindle, forming a network of fibers that connect the centromeres of the chromosomes.

Spindle orientation is regulated by a conserved set of molecules in metazoans. (A) The C. elegans one-cell embryo is polarized along the anterior-posterior axis and divides asymmetrically in a somatic anterior cell (AB) and a posterior germline precursor cell (P1). The conserved PAR (partitioning defective) proteins are localized asymmetrically at the cortex: PAR-3, PAR-6, and PKC-3 at the The spindle fibers play a crucial role in ensuring that each chromosome is correctly positioned and separated during cell division. When faulty spindle fibers fail to properly align the chromosomes, errors such as unequal distribution of genetic material or incomplete separation can occur. These errors can lead to aneuploidy and chromosomal Significance of Spindle Fibers in Meiosis: Spindle fibers are indispensable for the meiotic process. Their absence or malfunction can impede meiosis, leading to the non-formation of haploid cells. This disruption can consequently hinder sexual reproduction and the generation of genetic diversity. Role in Specific Phases of Meiosis: Meiosis I: