72 DNA Replication Biology Diagrams What is Helicase? Helicases are a class of enzymes that play a fundamental role in unwinding nucleic acids, either DNA or RNA, depending on the type of helicase involved.These enzymes are essential for various cellular processes, including replication, repair, transcription, and translation.Helicases were first identified in E. coli in 1976, and later, eukaryotic DNA helicases were discovered

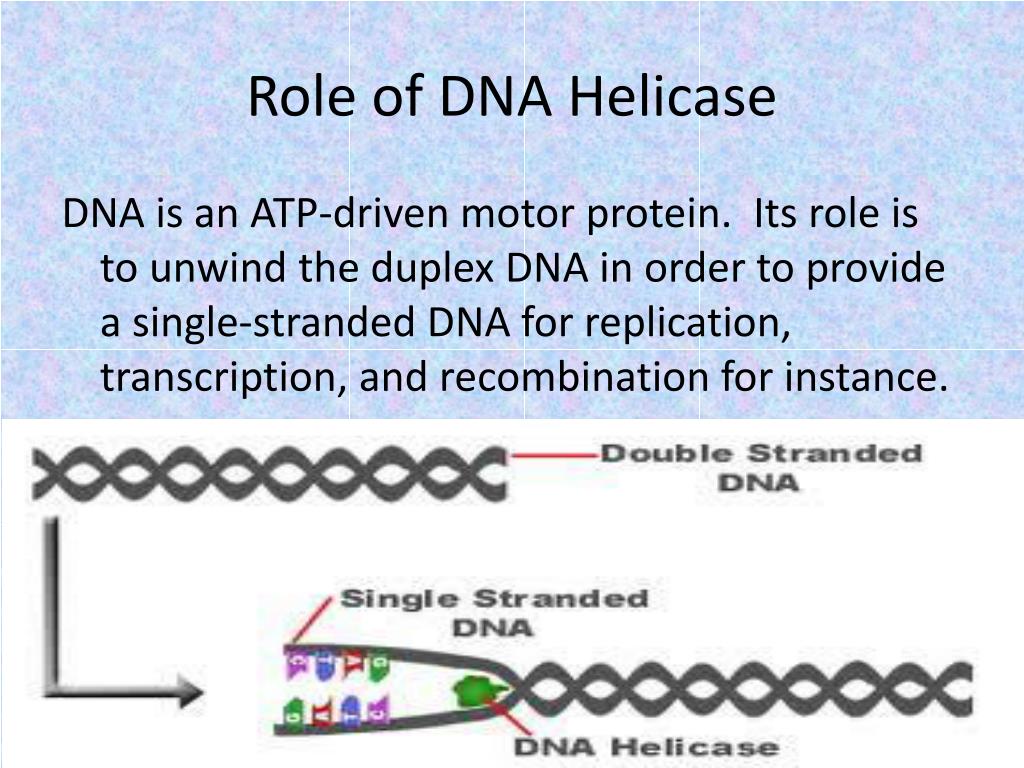
DNA helicase is a crucial enzyme in molecular biology, playing an essential role in DNA replication, repair, and transcription. As a motor protein, it unwinds the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) into single strands, enabling cellular processes that require access to the genetic code.

Helicases: Key Players in DNA Replication, Repair, and Transcription Biology Diagrams
Helicase plays a crucial role in the DNA replication process. It is also known as Dna B protein. It is a ring-shaped hexamer containing six identical subunits. During the replication process, each of the single-stranded DNA helicases is loaded. Then the DNA replication occurs in the bi-direction, unwinding the strand and creating the V-shaped
DNA helicases are ubiquitous enzymes found in all domains of life and associated with nucleic acid metabolisms such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, DNA repair, recombination, ribosome biogenesis, and decay.. DNA helicase was discovered first in E. coli in 1976.. They are ATP (adenosine triphosphate) dependent separating enzymes that promote separation of the two parental
Special Issue: DNA Helicases: Mechanisms, Biological Pathways, and ... Biology Diagrams
Role in DNA Repair. Helicases play a significant role in DNA repair, ensuring the maintenance of genomic stability by addressing damage and errors that can arise from various sources, including environmental factors and replication stress. Their involvement in repair mechanisms highlights their adaptability and precision in responding to DNA In conclusion, helicase plays a crucial role in DNA replication by unwinding the DNA double helix and facilitating the cooperation with DNA polymerase. Its unwinding activity allows for the separation of the DNA strands and the formation of a replication fork, while its continuous movement prevents the reannealing of the separated strands.
